Understanding FDIC Insurance: What It Is And How It Works
As a responsible saver, you’ve likely heard about FDIC insurance, but do you really understand what it is and how it works? In simple terms, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a government agency that provides insurance coverage to protect your bank deposits up to a certain amount. But there’s more to it than just that.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the world of FDIC insurance and explain its importance, how it works, and what you need to know to ensure your hard-earned money is safe and secure. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding FDIC insurance is crucial to protecting your financial future. So, let’s get started!
FDIC insurance is protection for bank depositors in the event of a bank failure. FDIC insurance covers deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per FDIC-insured bank, for each account ownership category. This includes checking, savings, money market accounts, and CDs. If a bank fails, the FDIC will step in to ensure that depositors receive their insured funds. It is important to note that FDIC insurance does not cover investments or other financial products offered by banks.
Understanding FDIC Insurance: What It Is and How It Works
FDIC insurance is a type of protection that safeguards depositors’ funds in the event that their bank fails. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is an independent agency that was established in 1933 in response to the Great Depression. It provides insurance coverage for deposits in case a bank goes bankrupt or becomes insolvent.
What is FDIC Insurance?
The FDIC is an independent agency of the federal government that provides deposit insurance to protect depositors in case a bank fails. FDIC insurance covers deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category. This means that if you have $250,000 or less in a single account at a bank, you are fully insured by the FDIC.
FDIC insurance covers all types of deposit accounts, including checking accounts, savings accounts, money market deposit accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs). It also covers deposits in different ownership categories, such as single accounts, joint accounts, and trust accounts.
How Does FDIC Insurance Work?
FDIC insurance works by protecting depositors’ funds in case their bank fails. If a bank fails, the FDIC takes over the bank’s assets and liabilities, including all deposits. The FDIC then pays depositors up to the insured amount per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category.
For example, if you have $200,000 in a single account at a bank that fails, the FDIC will pay you $200,000 in insurance coverage. If you have $300,000 in a single account at a bank that fails, the FDIC will pay you $250,000 in insurance coverage, and you will be uninsured for the remaining $50,000.
Benefits of FDIC Insurance
The primary benefit of FDIC insurance is that it protects depositors’ funds in case their bank fails. This means that depositors can be confident that their money is safe and secure in a bank that is insured by the FDIC. FDIC insurance also promotes financial stability by providing a safety net for the banking system.
Another benefit of FDIC insurance is that it is free for depositors. Banks pay premiums to the FDIC to fund the insurance coverage, but depositors do not have to pay anything for the coverage. This means that depositors can enjoy the peace of mind that comes with FDIC insurance without having to pay any additional fees.
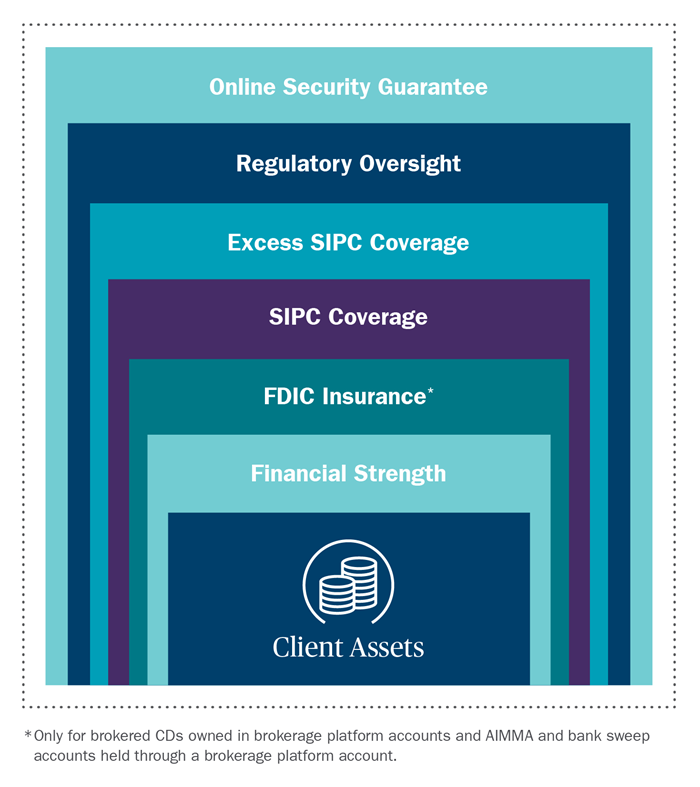
FDIC Insurance vs. SIPC Insurance
It is important to note that FDIC insurance is different from SIPC insurance. FDIC insurance protects depositors’ funds in case a bank fails, while SIPC insurance protects investors’ funds in case a brokerage firm fails.
SIPC insurance covers up to $500,000 per customer, including $250,000 in cash, in case a brokerage firm fails. However, SIPC insurance does not cover losses due to market fluctuations, fraud, or bad investment advice.
FDIC Insurance Limits
FDIC insurance limits are set by law and are subject to change. Currently, the standard insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category. This means that if you have $250,000 or less in a single account at a bank, you are fully insured by the FDIC.
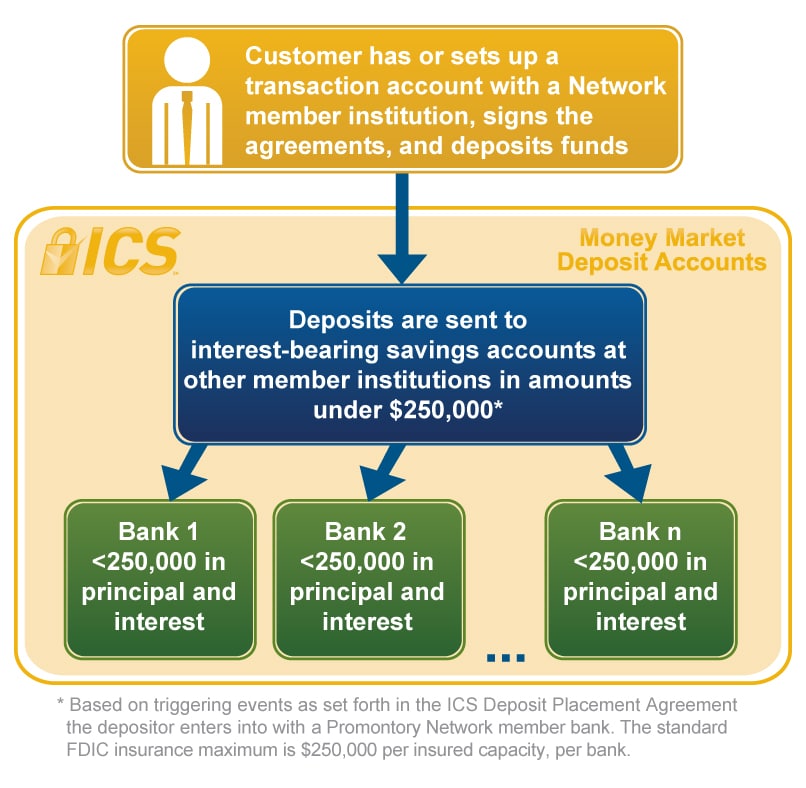
If you have more than $250,000 in a single account at a bank, you can still be fully insured by the FDIC if you have funds in different ownership categories. For example, if you have $500,000 in a joint account with your spouse at a bank, you are insured up to $500,000 because the joint account is a separate ownership category from your individual account.
FDIC Insurance Coverage for Retirement Accounts
FDIC insurance coverage for retirement accounts is the same as for other types of deposit accounts. The standard insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category.
However, there are some special rules for certain types of retirement accounts, such as IRA accounts. For example, if you have both a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA at the same bank, each account is insured up to $250,000 separately because they are different ownership categories.
FDIC Insurance and Bank Mergers
When two banks merge, the FDIC works with the banks to ensure that depositors are fully insured. If both banks are insured by the FDIC, depositors’ funds are automatically insured up to the standard insurance amount of $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category.
If one bank is not insured by the FDIC, depositors’ funds are insured up to the standard insurance amount for the insured bank. Depositors may also be able to increase their insurance coverage by opening accounts at different institutions.
FDIC Insurance and International Deposits
FDIC insurance does not cover deposits held in foreign banks or foreign branches of U.S. banks. However, some U.S. banks have foreign branches that are insured by the FDIC. Depositors should check with their bank to see if their foreign deposits are insured by the FDIC.
FDIC Insurance and Online Banks
FDIC insurance covers deposits in online banks just like it covers deposits in traditional brick-and-mortar banks. As long as the bank is insured by the FDIC, depositors are fully insured up to the standard insurance amount of $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category.
However, it is important to note that some online banks may be affiliated with traditional banks that have different names. Depositors should check to see if their online bank is insured by the FDIC and if it is affiliated with a traditional bank.
Conclusion
FDIC insurance is an important protection for depositors in case their bank fails. It provides insurance coverage for deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per institution, and per ownership category. FDIC insurance is free for depositors, and it promotes financial stability by providing a safety net for the banking system. Depositors should be aware of FDIC insurance limits and rules for different types of accounts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is FDIC insurance?
FDIC insurance is a type of deposit insurance that protects depositors in case their bank fails. If a bank fails and is unable to return depositors’ funds, the FDIC will step in and reimburse the depositors up to the insured amount. The standard insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per FDIC-insured bank, per ownership category.
FDIC insurance covers all types of deposit accounts, including checking, savings, money market, and CD accounts. It does not cover investments such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
How does FDIC insurance work?
FDIC insurance works by protecting depositors’ funds in case their bank fails. When a bank fails, the FDIC will step in and take over the bank’s assets and liabilities. The FDIC will then use the bank’s assets to pay off as much of its liabilities as possible.
If there are still funds owed to depositors, the FDIC will reimburse them up to the insured amount. The insured amount is $250,000 per depositor, per FDIC-insured bank, per ownership category. If a depositor has more than $250,000 in a single account, they can open additional accounts at the same bank or at different banks to increase their coverage.
Who is eligible for FDIC insurance?
All depositors at FDIC-insured banks are eligible for FDIC insurance. This includes individuals, businesses, and government entities. The standard insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per FDIC-insured bank, per ownership category. Depositors can increase their coverage by opening additional accounts at the same bank or at different banks.
Not all banks are FDIC-insured, so it’s important to check if a bank is insured before depositing funds. The FDIC provides a database of FDIC-insured banks on its website.
What is not covered by FDIC insurance?
FDIC insurance does not cover investments such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. It also does not cover losses due to fraud or theft. If a depositor’s funds are stolen or fraudulently withdrawn from their account, they should contact their bank and law enforcement immediately.
FDIC insurance also does not cover losses due to fluctuations in the stock market or other economic conditions. Depositors should be aware that FDIC insurance only protects against bank failures, not against losses due to investment decisions.
How can I check if my bank is FDIC-insured?
The FDIC provides a database of FDIC-insured banks on its website. Depositors can search for their bank by name or location to see if it is insured. The FDIC also provides a tool called EDIE (Electronic Deposit Insurance Estimator) that can help depositors calculate their insurance coverage based on their specific accounts and ownership categories.
Depositors should be aware that not all banks are FDIC-insured, so it’s important to check before depositing funds. If a bank is not FDIC-insured, depositors should consider other options for protecting their funds.

In conclusion, understanding FDIC insurance is crucial for anyone who wants to protect their finances. With the FDIC, you can rest assured that your deposits are safe and secure, even in the event of bank failure. By knowing the limits and requirements of FDIC coverage, you can make informed decisions about where to keep your money.
It’s important to remember that FDIC insurance only covers deposits in participating banks and savings associations, and only up to a certain limit. If you have more than the insured amount at one institution, you may want to consider spreading your money across multiple accounts or banks to ensure full coverage.
Overall, FDIC insurance serves as an important safeguard for consumers and helps promote stability in the banking industry. By taking the time to understand how it works and what it covers, you can make informed decisions about your finances and feel confident in the security of your deposits.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bank-47189639b37541338a6f383147cba708.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-can-i-easily-open-bank-accounts-315723-FINAL-3547624de9a648379a90fe38c68a2f7c.jpg)